If you have a habit of using a fabric mask from day to day without bothering to wash it, then after viewing this image, you will have to think again.
Recently, a study conducted by Eurofins Singapore Laboratory (a group of the same name that specializes in providing laboratories around the world) discovered a large number of bacteria and mold on the masks. washed for a long time.
Researchers did a comparison of the number of bacteria, molds, as well as Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus - associated with skin infections), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa - related to a rash). in reusable masks (referred to as reusable masks, such as fabric masks) and disposable masks after they have been used for 6 and 12 hours.
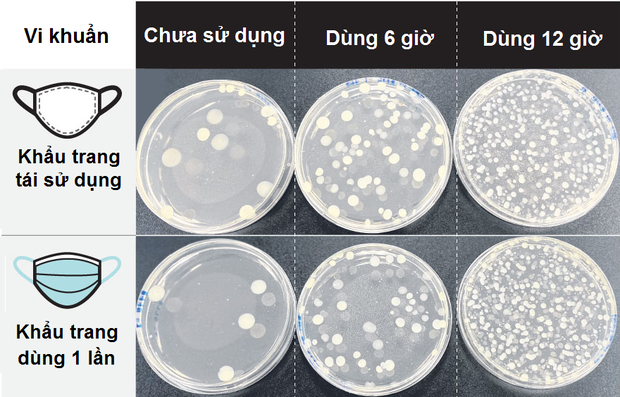
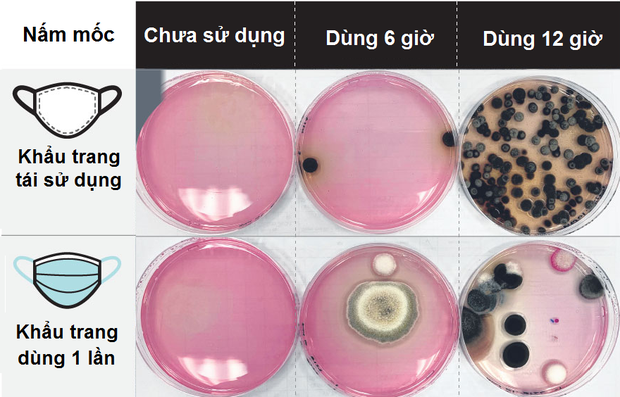
Although S. aureus and P. aeruginosa did not appear in any of the tests, mold and bacterial counts increased in both masks after they had been used for 12 hours. Responding to The Straits Times, the team's microbiologists said that a warm and humid microbiological environment in all types of masks is often beneficial for the bacteria to thrive.
In particular, reusable masks have more bacteria and fungi than disposable masks. Explaining this, Dr. Joel Lee, Rector of the University of Chemistry and Life Sciences (Nanyang Polytechnic University, Singapore) said the key is the material of the mask.
The main difference between disposable and reusable masks is the material of the inner layer closest to the mouth. "This inner layer is very easy to be where the bacteria are coughing or sneezing in, or they can be sprayed into drops when we talk while wearing a mask," says Dr. Lee shared.
The disposable respirator provides better bacterial filtration and air permeability, while the reusable mask is made of textile material, the greater the spacing between the fibers, thus providing the ability to filter out bacteria. worse.
Harmful bacteria reside on reusable masks for long periods of time without washing
The team also experimented with a reusable mask that was worn for a total of 6 hours, not washed for a week, and the numbers of bacteria, yeasts and molds were surprisingly high.
"Masks that aren't washed regularly can pick up dirt, sweat, and other bacteria," adds Dr. Lee. This may cause sensitization, skin irritation or infection.

Dr. John Chen, Assistant Professor at the Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine (National University of Singapore) said the bacteria on the mask could hardly lead to something serious in " Most of the time, "but the presence of bacteria on a regular basis can be quite worrying.
Such bacteria that reside on healthy skin can grow in large quantities on dirty masks and cause illness. "In small amounts, your immune system will keep them (bacteria on the mask - PV) under control (not causing disease - PV), but in large quantities they can cause a reaction." mild to severe allergies, respiratory problems and even nasal infection ".
Because it is difficult to determine if there are harmful bacteria on masks, people need to wash masks as often or after each use if possible, Chen recommended.